Cold forging
Cold forging
Forging is a method of transforming a forging from plastic deformation to another shape by means of impact or extrusion, without changing the quality and material composition of the workpiece to achieve the desired shape and machinery. Features, etc.
From the point of view of the use, "the parts that are required to have strength or rigidity in the parts of machinery, structures, and appliances, and the forming techniques of various thicknesses, rods, or blocks are collectively referred to as forging." /> The ultimate goal of forging is to destroy the coarsely cast structure, make it fine-grained, and compress the tiny gaps in the billet to improve the mechanical properties. The tensile strength of the forging in the direction of the forging line can be increased by about 1.2~1.3 times, the impact value. It is 2~4 times; in terms of forging, the purpose is to transform the billet into various products with metal flow and desired shape, of course, the shape of the workpiece needs to be complex when forging. The forging process is divided into several times.
Cold Forging Material is a method of forging that is not heated and is carried out at normal temperature or near normal temperature. It can save materials, improve productivity and speed, and has strong product strength, improved drop point or improved machinability. It is better than many other processing methods. In many cases, there is almost no need for subsequent processing or only polishing, but it is better than other presses. The tool (module) bears the load close to its strength. In order to make the material large deformation, the working conditions are harsh, and there are slight errors, the expensive tools (modules) are reimbursed. Therefore, the tool (module) design is a very important development program for cold forging.
There are many requirements for the size, shape, use and mechanical structure of cold forged products. There is no theory to follow. This technology requires years of experience. These accumulated experiences are the core technology and secrets of each cold forging factory.
The forgings obtained by forging process can improve the grain structure (continuous grain flow) by forcing the plastic deformation of the material during the forging process, making the material fine and homogenized, and obtaining excellent fatigue resistance, toughness and resistance. It is extremely suitable for the manufacture of various high-strength metal products or components due to mechanical properties such as impact. At the same time, because it can save the subsequent cutting process, its energy and material consumption is 1/3~1/5 of general machining.
Forging future role
The global economy in the production, hand tools, hardware parts or transportation related machinery and equipment, there will be a large demand for high-strength parts under unit weight, so the advantages of forging, the large and cheap supply of market and client parts, should be a few days ago Forging the most important tasks. Not only that, but with the heat treatment to improve the material, and then continue to develop or provide new products that have superior functional characteristics under more severe conditions.
Cold forging process
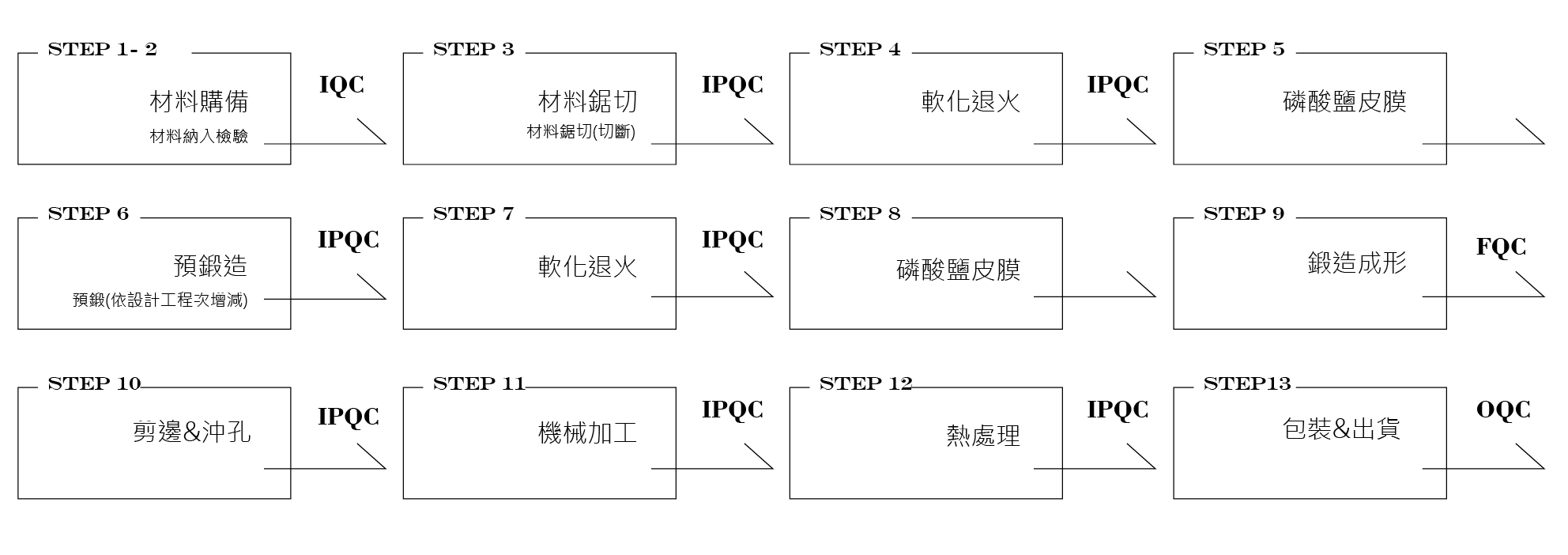
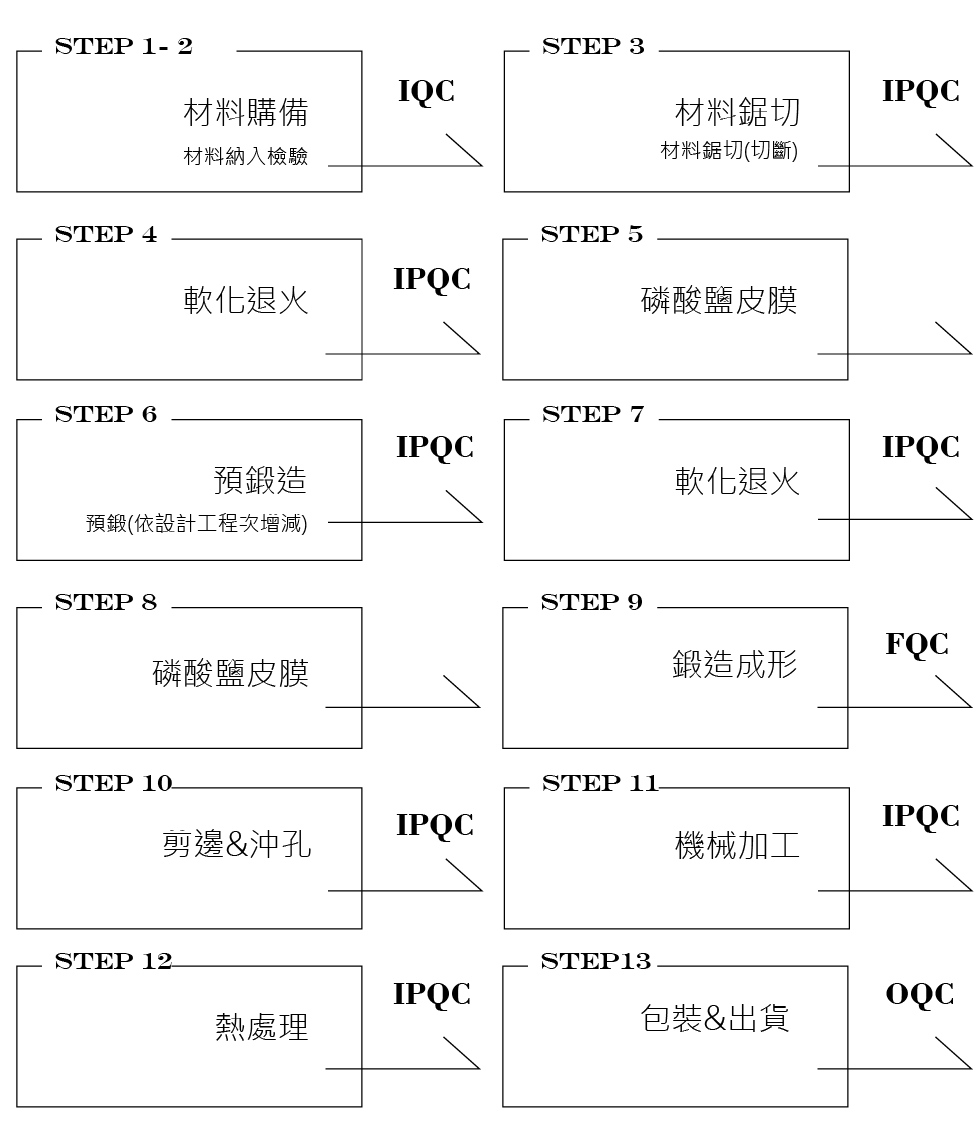
Forging works vary with the forging blanks, and the process is complex and varied; the typical forging process requires the following steps:

Advantages
- Can make large deformation processing
- Materials can be improved
- Strengthen with forging streamlines
- Massive productivity
- Various and small production flexibility
Disadvantages
- The load on the tool or machine is large
- The price of forging materials is high
- The operating environment is poor
- Long job change time
- High level of experience and proficiency